| Communication protocols EtherNet/IP: The "Digital Link" of Industrial Automation

In the wave of Industry 4.0, the real-time communication between devices is like the neural network of the human body, which determines the efficiency and accuracy of intelligent manufacturing. EtherNet/IP(Ethernet Industrial Protocol), as one of the core communication standards in the field of industrial automation, with its high bandwidth, real-time, open and multi-protocol compatibility, has become a "digital link" connecting traditional industrial equipment and future smart factories. It not only carries the flood of industrial data, but also plays a key role in equipment collaboration, remote control and system integration.
EtherNet/IP: The transformation from office networks to industrial sites
EtherNet/IP was born out of the innovative needs of industrial communication, and its core is to introduce standard Ethernet technology into the industrial field to solve the bandwidth and real-time bottlenecks of traditional protocols (such as DeviceNet, ControlNet). Different from the field bus such as PROFIBUS, EtherNet/IP is based on the TCP/IP protocol stack, which supports the transmission rate of 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps, and uses CIP(General Industrial Protocol) as the application layer protocol to achieve the unification of device configuration, control and information exchange.
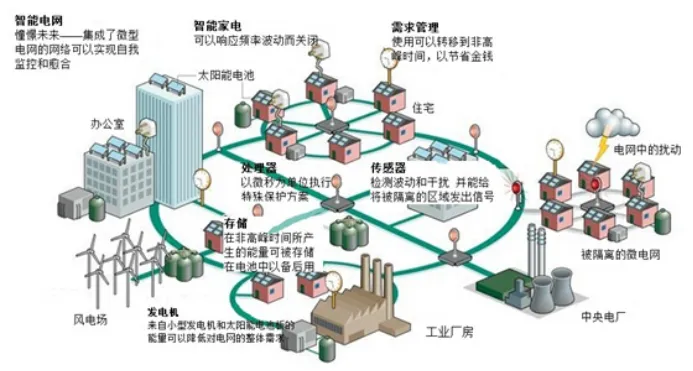
Three major breakthroughs in technological transition:
Real-time and non-real-time data hierarchical processing: Through priority division, key control instructions (such as PLC signals) are preferentially transmitted, and the response time can be as low as milliseconds to meet the needs of high-precision scenarios such as robot collaboration.
Openness and multi-manufacturer compatibility: Support different brands of equipment (such as Rockwell PLC, Siemens controller) seamless integration, GSDML file standardized configuration, debugging efficiency increased by more than 50%.
Flexible network architecture: Support star, ring and other topologies, combined with wireless gateway (such as DTD418M), can connect mobile devices (such as AGV), adapt to complex workshop layout.
Second, the core of technology: speed, security and intelligence integration
The "dual channel" mechanism of real-time communication
Explicit Messaging: Used for non-real-time data (such as device diagnosis and parameter configuration), ensuring reliability based on the TCP protocol.
Implicit Messaging: For real-time I/O data (such as sensor signals), based on the UDP protocol to achieve high-speed transmission, latency as low as 1 ms.
The "Triple Line of Defense" of Cyber security
VLAN isolation: The virtual LAN is used to prevent unauthorized devices from accessing the VLAN.
Data encryption and authentication: Supports IPsec to prevent data tampering and theft.
Redundancy design: Ring topology combined with dual network card redundancy, single point of failure does not affect the overall operation.
Deep synergy with emerging technologies
5G convergence: Transmits EtherNet/IP data in the 5G network through VXLAN tunnel technology to solve the delay and packet loss problems of traditional wireless communication.
Ai-driven: Combined with big data analysis, predictive maintenance of equipment (such as motor overheating warning) is achieved to reduce downtime losses.

3. Application scenario: Full link from sensor to cloud
Precision Manufacturing: The "conductor" of multi-axis collaboration
Case: In the automotive production line, ABB robots synchronize with Rockwell PLC in real time through EtherNet/IP to complete the engine cylinder head assembly, the error is controlled within 0.1mm, and the efficiency is increased by 30%.
Process Industry: "Safety guard" in explosion-proof area
Example: In chemical explosion protection areas, EtherNet/IP PA(Process automation variant) connects magnetostrictive displacement sensors to DCS systems, replacing traditional 4-20 mA signals and reducing the risk of manual inspection.
Smart Logistics: The "invisible dispatcher" of AGV fleets
Case: A warehouse center uses EtherNet/IP and 5G fusion technology to dispatch 200 AGVs to work together, shorten the response time of path planning to 50 ms, and reduce maintenance costs by 25%.
Interconnect across Protocols: A translator who breaks down ecological Barriers
Case: The application of EtherNet/IP to Profinet gateway in crude oil flowmeter realizes data interworking between Rockwell equipment and Siemens system, eliminating communication barriers caused by protocol differences.

Challenges and the Future: From deterministic communication to the Industrial Metauniverse
Technical challenge
Pressure from the data deluge: The proliferation of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices is placing higher demands on network bandwidth and real-time performance.
The threat of security vulnerabilities: industrial network attacks are frequent, and it is necessary to strengthen the security protection of edge computing nodes.
Future trend
5G+TSN(Time Sensitive Network) : Combined with the time synchronization mechanism of 5G URLLC(ultra-reliable low latency communication) and TSN, it can achieve microsecond level deterministic communication and support more mobile device access.
Digital twins and Industrial metauniverse: Map physical device states in real time via EtherNet/IP, build virtual factories, and optimize production processes and energy management.
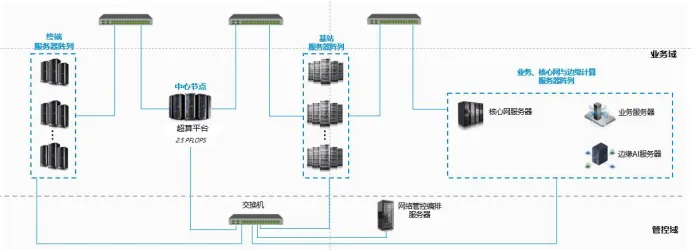
From sensors at the bottom of the shop floor to intelligent analysis platforms in the cloud, EtherNet/IP is the core pillar of industrial digital transformation with its open, efficient and secure characteristics. It is not only the innovation of protocol, but also the evolution of industrial thinking - in the flow of data, the factory is endowed with "perception, decision, evolution" intelligence.
"Between the bits of EtherNet, EtherNet/IP is weaving the future of industry."

Tianjin Changdatong Technology Co., LTD

















Please first Loginlater ~